If You Sigh a Lot: Causes and Treatment
Sighing can be explained as an inhalation which is involuntary and almost double than the standard tidal volume that is taken in. Studies have defined it as an inhalation that is twice in depth when compared with an average inhalation of a person.
Sighing is mostly done with the use of mainly the dorsal muscles and the upper chest and can be categorized as thoracic or chest breathing. It could also be present in adults and infants when they sleep. A study has revealed that normal adults resorted to occasional sighing during their sleep, ranging from one to twenty five sighs a night.
It may be a sigh of grief or it may be a sigh of relief; we all sigh sometime during a week if not once every day, at least. When we sigh, we inhale more and that reduces the supply of oxygen to the brain, leading to slight hyperventilation. Yawning has a similar effect.
Symptoms and Causes of Sighing
Sighing is considered as an abnormal breathing symptom. Sighing more frequently is regarded as a panic disorder sign. It could be a result of states of anxiety, nervous disturbances, pain the lower back, dyspnoea or nervous instability. Studies have pointed out that people who suffer from depression sigh excessively. Sighing is also found to be more common among patients who have rheumatoid arthritis or depression as against healthy people. It is clear, then, that frequent sighing is a result of high stress levels.
Excessive sighing can occur when the respiratory center is reset. For example, this happens after you digest a meal. It could also happen during and after a bout of physical exercise. While there could be numerous reasons for sighing, the most likely cause is linked to hyperventilation. In an article called `Hyperventilation Syndrome’ written by Blashear in 1983, it has been suggested that doctors consider occasional sighing as a condition due to the hyperventilation syndrome.
When this happens, people hold their breath after the normal round of exhalation and subconsciously do breathing exercises to reduce the process of inhalation/exhalation as explained by the Buteyko method of breathing. This helps in increasing the supply of oxygen to the brain.
Other researchers have also revealed that sighing may be triggered by the mental load and the recovery from a focused task. It could be an expression of a desire or an activity that needs to be rejected.
In the case of infants, when they are not kept waddled, they will have a higher frequency of sighs during their sleep. This is mainly because swaddling tends to limit the ventilation and it helps prevent chest breathing. It also increases arterial carbon dioxide and the concentration of cellular oxygen, making the breathing patterns regular.
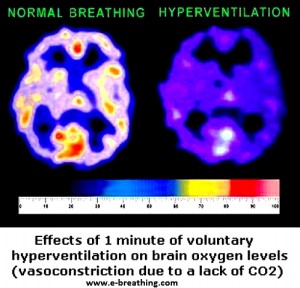
There are other explanations about the causes of sighing. They are thought to be as a result of spasms of diaphragm. Heavy chest breathing could lead to poor function of the diaphragm as there is insufficient lung tissue stimulation. There is also insufficient stimulation of the stretch receptors which are situated in the lower portion of our lungs. Sighing, in such cases, tries to give a little relief to these natural hyperventilation effects. Hyperventilation builds up alveolar hypocapnia and reduces the diaphragm oxygenation. The deficiency of carbon dioxide in arterial blood will lead to spasms in almost all the muscles of the body and that includes the diaphragm.
All hyperventilation causes like breathing through the mouth, supine sleep, high levels of stress or anxiety, poor posture and overeating could lead to the intensification of sighs. Sighing is also accompanied by hyperventilation symptoms like dyspnoea which is shortness of your breath. Excessive breathing has an important role to play in sighing pathophysiology. Therefore, frequent sighing indicates that a person is affected by hyperventilation. A large majority of people today are hyper ventilators and heavy chest breathers due to their life styles.
Effects of Occasional Sighing
The major impact of frequent sighing is a condition known as hypocapnia. It leads to a deficiency of carbon dioxide in the arterial blood, body cells and lungs. Fast and deep breathing will not help improve the oxygenation of arterial blood and bring it down to normal breathing. Some researchers feel that reduced tension in arterial carbon dioxide can be maintained with just occasional sighing that is superimposed with a little effort over the regular breathing patterns. However, occasional sighing also relates to a chronic condition of hyperventilation and reduced levels of oxygen in the cells. Excessive sighing will produce distressing effects on the oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the heart, brain and other important organs.
People who are suffering with acute breathlessness or dyspnoea have confirmed that sighing brings a little relief to the respiratory muscles. This is linked to mechanical effects on the diaphragm. Studies have also found that artificial sighing could lead to positive effects on the oxygenation of arterial blood.
Some people have informed the researchers that they sigh only when they feel dissatisfied or discontent. Others sigh when they get frustrated when they are not able to comprehend something and find things difficult to understand. When people get disgruntled as a result of some ignorant comments by others, they also tend to sigh. They have all confirmed that sighing occurs subconsciously when they get upset or become too anxious. It was confirmed by several studies that sighing is definitely associated with negative moods in most people. It indicates signs of frustration, boredom and disappointment.
Treatment of Causes of Excessive Sighing
As a measure for the body-oxygen tests, people who sigh more frequently have twenty seconds or less during the test. If they are able to achieve more than thirty seconds, they will be able to rid themselves from the symptoms of frequent sighing. Before the test, the subject is advised to rest. A normal exhalation is recommended with the mouth closed and the nose pinched. The seconds are then counted before the body gives out the initial impulsive breathing desire. People feel a movement in the abdomen or a swallowing sensation in their throat at this juncture. The number of seconds that are counted before this point is the oxygen level measure.
It has been proved that sighing will disappear rapidly with the use of breathing devices which are resistive. The devices available are the DIY (Do-It-Yourself) breathing device, Samozdrav and the Frolov device. All these devices have a positive effect over the causes of excessive sighing. They help increase the levels of carbon dioxide in the airways and they will also help stimulate the respiratory muscles and the lungs.
Corrections in physical exercises and appropriate changes in lifestyles will also be necessary to achieve remission from excessive sighing.