Tidal Volume: Normal, Ideal, in Disease
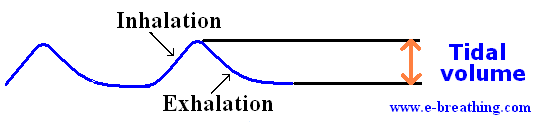
The chart above shows volume of the lungs as a function of time. Tidal volume is a difference between volumes at normal inhalation and normal exhalation.
Normal tidal volumes are much smaller in newborn, infants, and children, down to 150 ml due to their smaller lung sizes.
This value is small that normal (or healthy) people do not notice and have nearly no sensations related to their automatic breathing.
What about tidal volume in people with chronic diseases?
This means that during exercise, humans usually breathe in (or breath out) about 2 times less than their vital capacity.
People with mild forms of heart disease, cancer, diabetes, asthma, COPD, and many other conditions have about 15-20 breaths per minute with 12-18 L/min for minute ventilation at rest. These numbers allow us to calculate their usual tidal volume: about 700-900 mL.
Therefore, they suffer from deep breathing..
[end_tabset]

